We often refer to the PCB (printed circuit board) plays an important role in the electronics industry. PCBs build a bridge to the world of electronics, so to speak, and the core material and prepreg of PCBs assist in the construction of printed circuit boards.
In this article will take you to understand what is PCB core and Prepreg material, and the differences between them and the application.
What is Prepreg material?
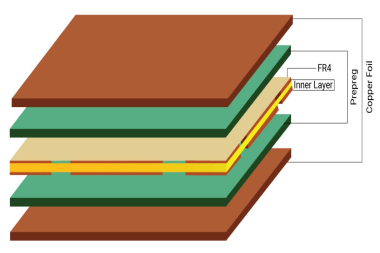
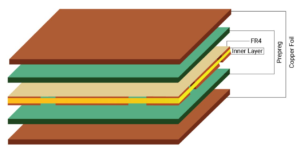
Simply put, Prepreg is a glass fiber with a resin binder impregnation. It is a dielectric material used to provide proper insulation between copper and PCB Core.
Prepreg is also commonly refers to as a bonding material that either combines two cores or a core and a copper foil. This plays a crucial role in PCB design and manufacturing.
The different types of prepreg depend on their thickness and the amount of resin they hold, the higher the resin they contain, the higher the price.
- Standard resin (SR)
- Medium resin (MR)
- High resin (HR)
The process of manufacturing Prepreg
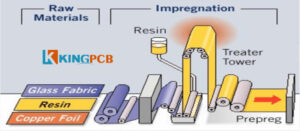
Why is Prepreg so important in the PCB manufacturing process?
- Easy to apply
- Facilitates waste management in the manufacturing process
- Multiple Prepreg options available to meet different needs
- Helps reduce the weight of equipment
What is a PCB core material?
A PCB core consists of a FR4 (flame retardant) rated glass fiber epoxy laminate with copper laminated on both sides. It is a rigid base material with copper laminated to the instrumentation used to manufacture single-sided, double-sided and multilayer circuit boards.
The difference between PCB core material and Prepreg material
Simply put, core material is the product of prepreg and lamination. As such, it is much more rigid compared to prepreg. Prepreg is partially dry without lamination and is not as rigid as core. The core consists of a glass fiber epoxy laminate which is flame retardant and has copper on both sides.
Another important difference between PCB prepreg and core is its dielectric constant. While the dielectric constant of the core does not change, the dielectric constant of the prepreg changes before and after lamination. The different dielectric constants are also a function of the following factors.
- Resin content
- Resin type
- Glass braid
Explore KingPCB’s services
PCB cores and Prepreg are both important components of PCBs, and understanding these basics is critical to PCB manufacturing.
With over 10 years of combined experience in PCB manufacturing and assembly services, KingPCB offers advanced assembly technology and advanced PCB solutions. More than just high quality, we also offer the most competitive prices.
Don’t hesitate to contact us now to learn more about our PCB services